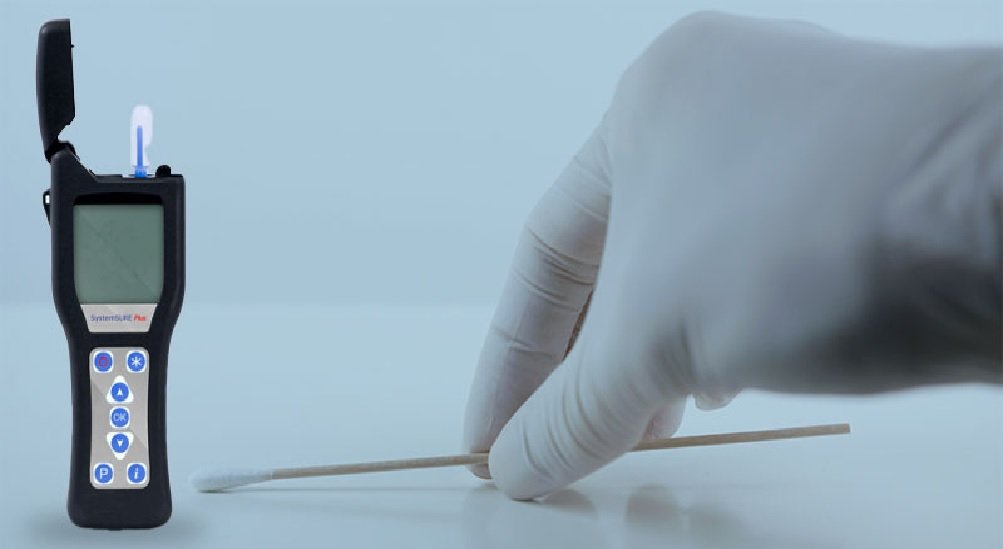
In today’s world, maintaining high hygiene standards is essential across various industries, particularly in food service, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals. One effective method for monitoring cleanliness is ATP swabbing. This technique measures adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a molecule found in all living cells, providing valuable insights into the cleanliness of surfaces and equipment.
What is ATP?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide that serves as a primary energy carrier in cells. It is present in bacteria, viruses, and even food residues. The presence of ATP on a surface indicates biological material, which can suggest potential contamination. By measuring the levels of ATP, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their cleaning protocols and ensure that surfaces are safe for use.
The ATP Swabbing Process
ATP swabbing involves a straightforward procedure. First, a swab is moistened with a reagent solution that releases ATP from the surface being tested. The swab is then rubbed over a specific area, typically 10 cm by 10 cm, to collect any biological material present. After swabbing, the swab is inserted into a luminometer, which measures the light produced by a reaction between ATP and the reagent. The amount of light emitted correlates with the concentration of ATP, providing a quantifiable measure of cleanliness.
Applications of ATP Swabbing
- Food Industry: In food processing and service, maintaining hygiene is critical to prevent foodborne illnesses. ATP swabbing helps monitor surfaces, equipment, and utensils, ensuring that they are adequately cleaned and sanitized. Regular testing can identify problem areas and reinforce cleaning protocols.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics face strict regulations regarding cleanliness to protect patients from infections. ATP swabbing is used to test surgical instruments, patient areas, and high-touch surfaces, helping to maintain a sterile environment.
- Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, any contamination can have serious implications. ATP swabbing is employed to ensure that production areas, equipment, and containers are free from biological contamination, thus adhering to strict industry standards.
Benefits of ATP Swabbing
- Rapid Results: One of the primary advantages of ATP swabbing is the speed of results. The process can be completed in a matter of minutes, allowing for immediate feedback on cleaning effectiveness. This quick turnaround enables staff to take corrective actions promptly.
- Quantitative Data: Unlike visual inspections, which can be subjective, ATP swabbing provides quantitative data. This allows for consistent monitoring over time and helps identify trends in cleanliness, making it easier to implement necessary changes in cleaning procedures.
- Ease of Use: The ATP swabbing process is relatively simple, requiring minimal training for staff. This ease of use ensures that businesses can incorporate it into their routine cleaning protocols without significant disruptions.
Limitations of ATP Swabbing
While ATP swabbing is a valuable tool, it is not without limitations. For example, ATP does not differentiate between living and dead organisms, meaning that a high ATP reading could indicate contamination from organic material rather than active pathogens. Additionally, the presence of certain disinfectants can affect ATP measurements, potentially leading to misleading results. Therefore, it is essential to use ATP swabbing as part of a comprehensive cleaning and monitoring strategy.
Conclusion
ATP swabbing is a vital tool in ensuring hygiene across various industries. By providing quick and quantitative feedback on cleanliness, it helps organizations maintain high standards and protect public health. While it has its limitations, when used alongside other monitoring methods, ATP swabbing can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of cleaning protocols, ensuring safer environments for employees and customers alike.
Click the link below to find out more!